Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is difficult to diagnose due to overlapping symptoms with other neurodegenerative disorders, often leading to delays in treatment and clinical trial enrollment. This technology identifies a unique panel of 13 circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) in blood plasma, which serve as biomarkers for FTD. Using next-generation sequencing and machine learning, the method enables early, accurate diagnosis and improves patient selection for clinical trials.
- Early and accurate FTD diagnosis – Reduces misdiagnosis and diagnostic delays
- Clinical trial stratification – Identifies FTD patients for drug development studies
- Monitoring drug response – miRNA biomarkers serve as pharmacodynamic indicators
- Non-invasive and cost-effective
- High accuracy, ~90% classification accuracy
- Supports clinical decision-making and trial enrollment
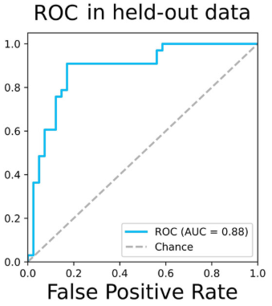
Diagnosis of FTD by a distinctive cell-free miRNA signature
The technology has been validated in a cohort of 168 FTD patients and 125 controls using next-generation sequencing and machine learning, demonstrating high diagnostic accuracy. It is in the preclinical stage with strong potential for clinical translation.


