18679
Overview
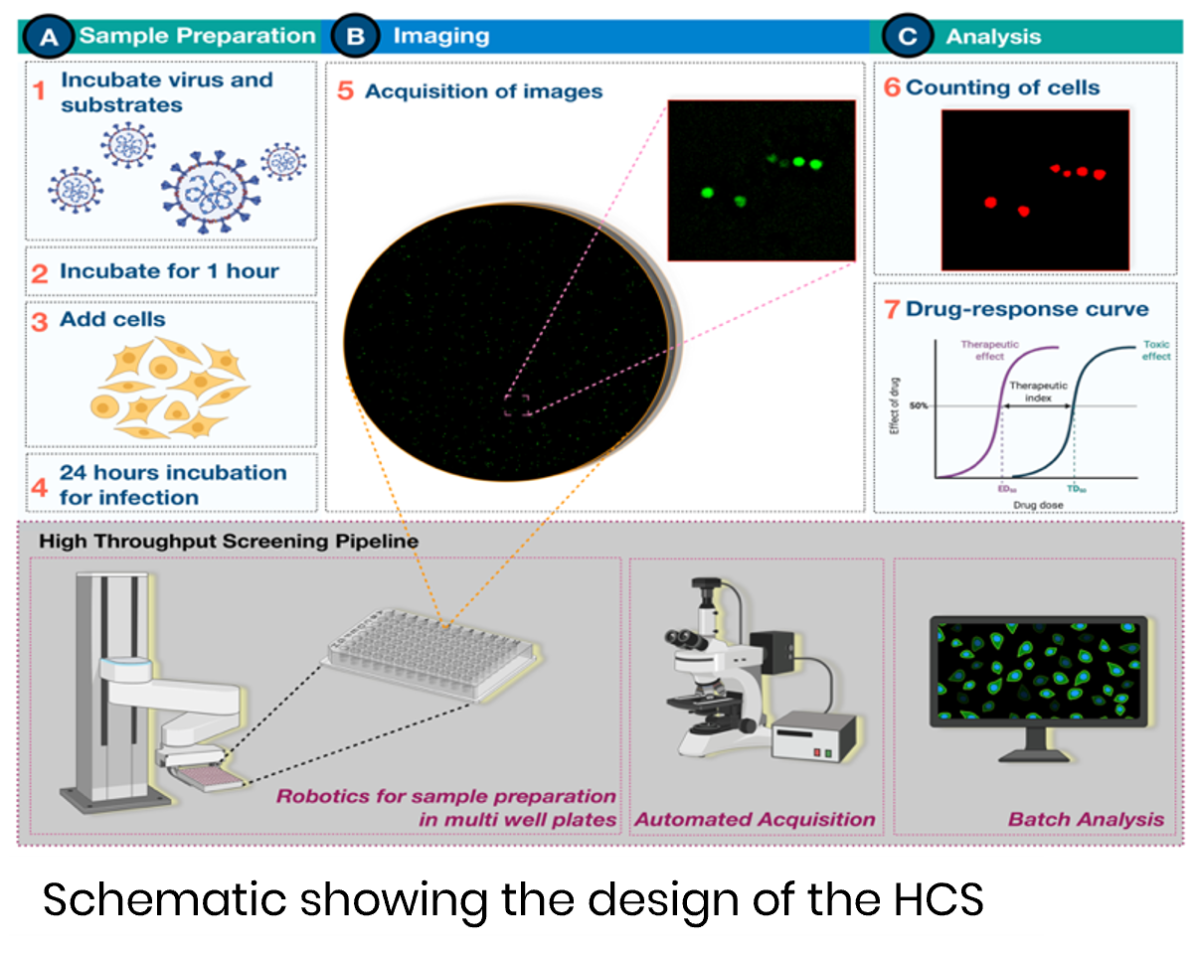
Emerging and re-emerging enveloped viruses, such as SARS-CoV-2, influenza, Nipah, and Ebola, continue to pose serious global health threats, with limited treatment options. A novel screening platform enables rapid discovery of small molecules that inhibit viral membrane fusion—a conserved and essential step in viral infection, offering a promising strategy to combat both current and future pandemics.
Applications
- High-throughput screening for viral membrane fusion inhibitors
- Discovery of novel antivirals targeting SARS-CoV-2 and related viruses
- Development of broad-spectrum antivirals against future pandemic threats
- Identification of small molecules with unique antiviral mechanisms
- Developing antivirals for animal infections, including feline viral diseases (e.g., FIP in cats)
Differentiation
- High signal-to-noise ratio and single-cell resolution
- Automated, scalable platform suitable for high-content screening
- Targets a conserved viral mechanism, enabling broad-spectrum potential
- Discovery of compounds with novel mechanisms of action
Development Stage
~200,000 compounds screened using the platform. Several novel fusion inhibitors identified; hit-to-lead optimization currently underway.
Patent Status:
PCT Published: Publication Number: WO 2025/057164
Contact for more information


